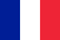
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine occurs due to pathological changes in intervertebral discs. They weaken, become thinner, lose elasticity, ceasing to protect the vertebrae from damage and losing the ability to provide them with sufficient mobility. The main danger of cervical osteochondrosis is that the disease affects the nerve endings of the spinal region, due to which there is a violation of the blood supply to the brain.
Types and classification
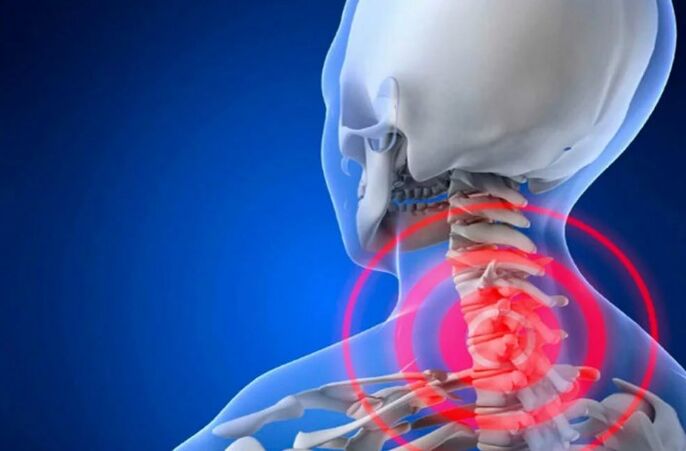
Several stages of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are distinguished:
- First: initial changes in the cartilage fabric of the intervertebral disc;
- second: the beginning of the thinning of the disk, a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae;
- Third: Destruction of the disk, the beginning of the deformation of the spine;
- Fourth: strong deformation of the spine.
Causes
The main cause of cervical osteochondrosis lies in the structure of the spine in this area. All the vertebrae here fit each other tightly and easily shift even with minor loads.
Given how mobile the cervical region is, it is not surprising that the disease is so widespread.
Provoke the onset of the disease:
- congenital anatomical features (in people with a long neck, osteochondrosis occurs more often);
- violation of the digestibility of minerals;
- hormonal deviations;
- lack of sufficient muscle corset in the neck and shoulders;
- hypodynamia;
- cervical injuries;
- hypothermia;
- posture disorders;
- Excess weight.
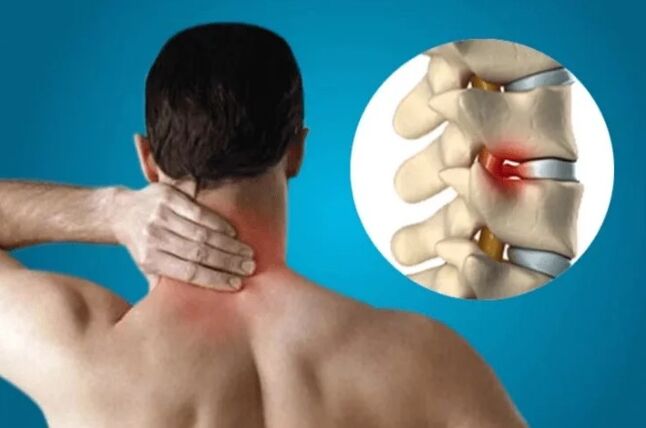
Symptoms
- Often the first symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is a headache. It can be very strong, flowing like migraines, accompanied by dizziness and madhouse.
- The appearance of "flies", dark spots, cloudings before the eyes, and a decrease in vision are characteristic.
- The pain in the neck with this disease gives to the back of the head, forehead, ears, it intensifies when the position of the head changes.
- Hand numbness is often noted.
- There is noise in the ears, hearing loss.
- A violation of coordination of movement, fainting may occur.
Diagnostics
To identify osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, they carry out:
- radiography that determines the condition of the vertebrae;
- computed tomography, to identify disk damage;
- Dopplerography that establishes blood flow disorders;
- Duplex scanning showing the state of blood vessels.
Treatment
As an ambulance for cervical osteochondrosis, painkillers and anti -inflammatory drugs are needed. Depending on the strength of the pain syndrome, local drugs (ointments and gels), tablets or injections are used.

Also appointed:
- vitamin therapy (vitamins of group B);
- drugs that relieve muscle spasm,
- Chondroprotector;
- physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, paraffin, magnetotherapy and others);
- medical gymnastics;
- Massage and self -massage.